Introduction
Biofuel is a renewable energy source that has the potential to reduce India’s dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change. India is a rapidly developing country that is facing a severe energy crisis. With increasing demand and depleting fossil fuel reserves, the country is exploring various alternatives, including biofuels. In this article, we will discuss the current status and future prospects of biofuel energy in India.

What is Biofuel Energy?
Biofuels are fuels that are derived from biomass, such as plant materials, agricultural waste, and forest residues. They are considered renewable energy sources as they are produced from organic matter that can be regrown. Biofuels can be classified into two categories: bioethanol and biodiesel. Bioethanol is produced by fermenting sugar and starch crops such as sugarcane, corn, and sweet sorghum. Biodiesel, on the other hand, is produced by the transesterification of vegetable oils such as soybean oil, mustard oil, and jatropha oil.
Current Status of Biofuel Energy in India
India has a vast potential for biofuel production due to its favorable agro-climatic conditions and abundant biomass resources. The government of India has taken several initiatives to promote biofuel production in the country. In 2018, the government launched the National Biofuel Policy, which aims to promote the use of biofuels in the transportation sector. The policy mandates the blending of ethanol with petrol and biodiesel with diesel.
The Indian government has set a target of 20% blending of ethanol in petrol and 5% blending of biodiesel in a diesel by 2030. Currently, India produces around 1.5 billion liters of ethanol and 0.4 billion liters of biodiesel annually. The majority of ethanol production is from sugarcane molasses, while biodiesel production is from non-edible oilseeds such as jatropha and Pongamia.

Future Prospects of Biofuel Energy in India
The future prospects of biofuel energy in India are promising. The government has set a target of achieving 10% ethanol blending and 2.5% biodiesel blending by 2022. To achieve this target, the government has launched several schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN Yojana and the Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) scheme. These schemes aim to promote the use of non-food feedstocks for biofuel production and establish a network of compressed biogas plants in the country.
Apart from the transportation sector, biofuels have the potential to be used in the power sector as well. Biomass-based power plants can generate electricity from agricultural waste and forest residues. The government has also launched the Biomass Power and Bagasse Co-generation Program, which aims to promote the use of biomass-based power generation in the country.
Types of Biofuel Energy
There are several types of biofuel energy that are commonly used today.
- Bioethanol: Bioethanol is a type of biofuel that is made from sugar, corn, or other crops. It is primarily used as a gasoline additive to reduce emissions and improve performance.
- Biodiesel: Biodiesel is a type of biofuel that is made from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled cooking grease. It can be used as a direct substitute for diesel fuel in diesel engines.
- Biogas: Biogas is a type of biofuel that is produced by the anaerobic digestion of organic matter, such as agricultural waste, sewage, or food waste. It is primarily used for electricity generation and heating.
- Biojet fuel: A type of biofuel used in aviation is called bio-jet fuel. It is made from plant oils, animal fats, or algae and can reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional jet fuel.
- Biochemicals: Biochemicals are chemicals that are made from renewable biomass sources. They can be used in a variety of applications, including plastics, solvents, and detergents.

Biofuel Energy: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Biofuel Energy:
- Renewable: Biofuels are made from renewable biomass sources, such as crops, animal waste, and food waste. This means they can be replenished and are not finite like fossil fuels.
- Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biofuels emit fewer greenhouse gases than fossil fuels, which helps reduce the impact of climate change.
- Energy Security: Biofuels can reduce dependence on foreign oil and provide energy security to countries.
- Job Creation: The biofuels industry can create new jobs in the agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation sectors.
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Biofuels can help diversify the energy mix and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Disadvantages of Biofuel Energy:
- Land Use and Deforestation: Biofuel production requires land, which can lead to deforestation and loss of biodiversity. This can also lead to food insecurity and displacement of local communities.
- High Water Use: Biofuel crops require a lot of water for growth and production, which can lead to water scarcity in some regions.
- Competition with Food Crops: Biofuel production can compete with food crops for land, water, and other resources, which can increase food prices and exacerbate food insecurity.
- Energy Intensive Production: Biofuel production requires a lot of energy, which can result in high greenhouse gas emissions if the energy is not from renewable sources.
- Limited Feedstock Availability: The availability of feedstock for biofuel production can be limited, which can lead to price volatility and potential shortages.
Overall, the pros and cons of biofuel energy need to be carefully considered before making any policy decisions. While biofuels can offer a renewable and sustainable energy source, they also have potential drawbacks that need to be addressed.
Biofuel Companies in India:
There are several biofuel companies in India, including:
- Indian Oil Corporation
- Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited
- Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited
- Praj Industries Limited
- Neste India
Current Research on Biofuels Energy in India:
India is actively involved in research on biofuels.
- Development of second-generation biofuels from lignocellulosic biomass
- Improvement of biomass yield and quality for biofuels production
- the use of algae as a feedstock for the creation of biofuels.
- Development of technologies for biofuel production from waste and residues
- Improvement of biofuels distribution and infrastructure in the country
Biofuel Industry
The biofuel industry in India is growing rapidly, with several initiatives taken by the government and private sector. The industry is expected to create new jobs and contribute to rural development by promoting agricultural growth. The Indian biofuel industry is expected to reach a production capacity of 10 billion liters by 2022.
Biofuel Production
India has a diverse range of feedstocks for biofuel production, including sugarcane, rice husk, wheat straw, jatropha, and algae. Ethanol and biodiesel are the two primary biofuels produced in India. Ethanol is primarily produced from sugarcane molasses and is blended with petrol. Biodiesel is produced from non-edible oilseeds, such as jatropha and Pongamia.

Biofuel Policy in India
The National Biofuel Policy was launched in 2018 to promote biofuel production in India. The policy aims to promote the use of biofuels, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. The policy provides various incentives and subsidies for biofuel production and use.
Biofuel Projects in India
India has several biofuel projects, including:
- Ethanol Blended Petrol Program
- Biodiesel Purchase Policy
- Bioenergy Village Projects
- Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) Initiative
Overall, the biofuel industry in India is rapidly growing and has the potential to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote sustainable development.
Is Biofuel Renewable?
Yes, biofuels are considered renewable because they are made from biomass, which can be replenished through sustainable agricultural practices. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and non-renewable, biofuels can be produced indefinitely as long as there is a supply of biomass.
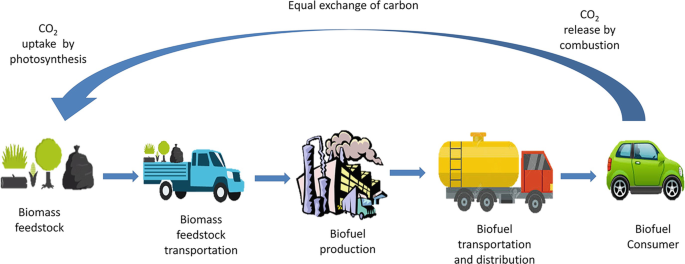
How Does Biofuel Work?
Biofuels are produced by converting biomass into a usable form of energy. This is typically done through a process called fermentation or gasification. Fermentation involves breaking down the carbohydrates in biomass into sugars, which are then fermented to produce alcohol, such as ethanol. Gasification involves heating biomass in the presence of oxygen to produce a gas that can be burned for energy. The resulting biofuels can be used as a replacement for fossil fuels in transportation, heating, and power generation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biofuel energy has immense potential to reduce India’s dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change. The government of India has taken several initiatives to promote biofuel production in the country. The future prospects of biofuel energy in India are promising, and with the right policies and incentives, India can become a leading biofuel producer and consumer in the world.
Read More:- The Power of Nuclear Fuel Energy for the Future.






