The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is all set to embark on its next lunar mission, Chandrayan 3 Launch. Chandrayaan-3 aims to further explore the Moon and enhance our understanding of its surface. In this article, we delve into the details of Chandrayaan-3, its motive, and the very advancements of technology it brings.

I. Chandrayan 3 Launch Date, Time and Place
Date:-14-07-2023
Time:- 02:35 PM
Place:-Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota
II. Overview of Chandrayan 3 Launch
Chandrayan 3 Launch is an ambitious project by ISRO, aiming to land an unmanned spacecraft on the lunar surface. This mission will serve as a follow-up to Chandrayaan-2, which achieved significant milestones despite facing challenges during the landing phase. The objective of Chandrayaan-3 is to continue India’s exploration of the Moon and gather valuable scientific data.

III. Objectives of Chandrayan 3 Launch Mission
A. Lunar Surface Exploration: The primary goal of Chandrayaan-3 is to conduct detailed studies of the lunar surface. It aims to gather high-resolution images and data to analyze the Moon’s topography, mineralogy, and the presence of water molecules.
B. Technology Demonstration: Chandrayaan-3 will carry advanced technologies and instruments to demonstrate India’s capabilities in the field of lunar exploration. This includes testing new landing and rover technologies to improve future missions.
C. Enhanced Rover Mobility: Learning from the challenges faced during the Chandrayaan-2 mission, Chandrayaan-3 will feature an upgraded rover with enhanced mobility. This will allow for better navigation and exploration of the lunar surface.
IV. Key Components of Chandrayaan-3
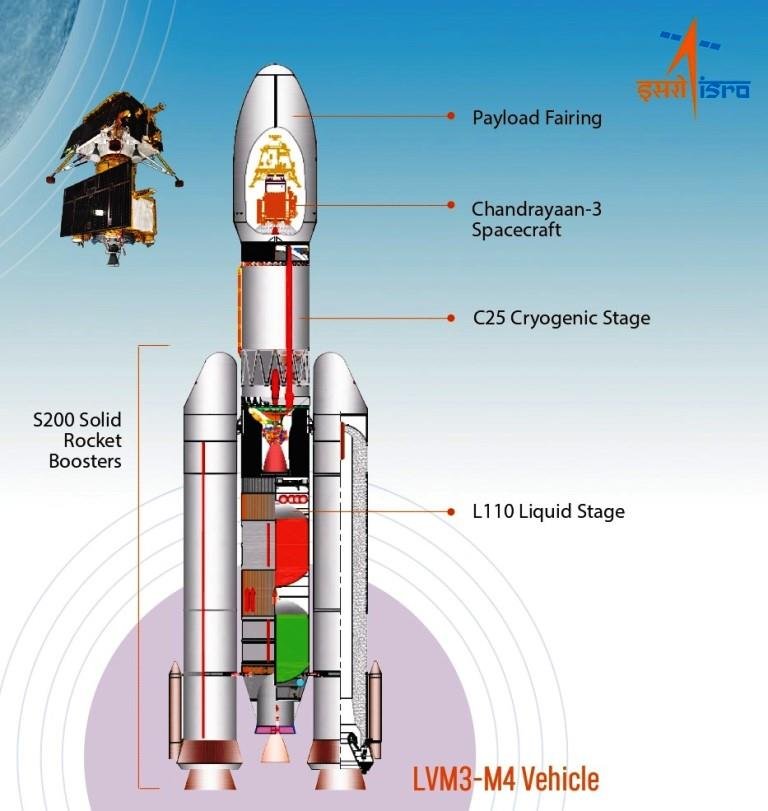
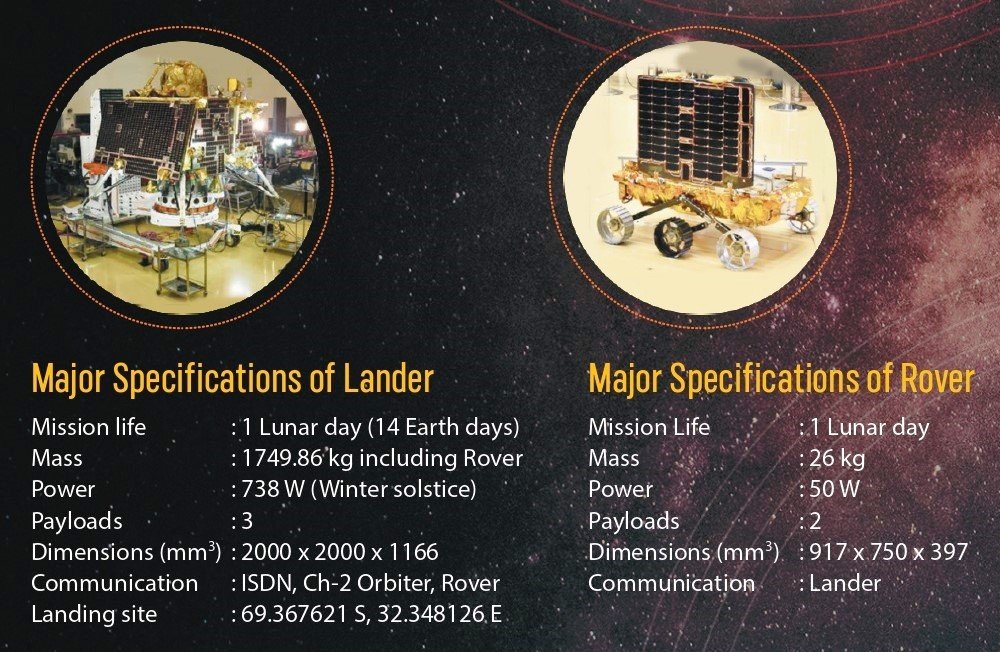
- Lander: The lander is a crucial component of Chandrayaan-3, responsible for the soft landing of the spacecraft on the lunar surface. It will house scientific instruments and the rover, enabling them to carry out their respective missions.
- Rover: The rover is a robotic vehicle designed to traverse the lunar surface. Equipped with scientific instruments, it will collect valuable data and transmit it back to Earth. The enhanced mobility of the rover will enable it to cover larger distances and explore diverse regions of the Moon.
- Orbiter: Although Chandrayaan-3 primarily focuses on the lander and rover, an orbiter will also be present. The orbiter will orbit the Moon and provide communication support between the lander/rover and Earth. It will also conduct remote sensing observations to aid scientific investigations.

V. Advancements in Chandrayaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 incorporates several advancements over its predecessor to ensure a successful mission. Some of the notable advancements include:
- Improved Landing Technology: ISRO has enhanced the landing technology to address the challenges faced during the Chandrayaan-2 mission. Lessons learned have been applied to improve the accuracy and precision of the soft landing process.
- Upgraded Scientific Instruments: Chandrayaan-3 will carry upgraded scientific instruments to capture detailed images and data. These instruments will provide valuable insights into the lunar surface and its composition, contributing to our understanding of the Moon’s evolution.
- Robust Communication Systems: The communication systems of Chandrayaan-3 have been strengthened to ensure reliable and uninterrupted communication between the spacecraft and Earth. This will enhance the overall mission efficiency and data transmission capabilities.
VI. The Conclusion of Chandrayan 3 Launch
Chandrayan 3 Launch, the upcoming lunar mission by ISRO, holds immense promise in expanding our knowledge of the Moon. With its objectives focused on lunar surface exploration, technology demonstration, and enhanced rover mobility, this mission is poised to contribute significantly to scientific advancements. The advancements in landing technology upgraded scientific instruments, and robust communication systems showcase India’s commitment to pushing boundaries in space exploration. As Chandrayaan-3 embarks on its journey, anticipation grows for the groundbreaking discoveries and insights it will unveil about Earth’s celestial neighbor, the Moon.

Chandrayaan-1 and Chandrayaan-2: India’s Lunar Missions Expanding Scientific Horizons
Chandrayaan-1 and Chandrayaan-2 are two historic lunar missions undertaken by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) with the aim of advancing scientific knowledge and technological capabilities in space exploration. These missions mark significant milestones in India’s space program, showcasing the nation’s growing prowess in the field and contributing valuable data to the global scientific community.
I. Chandrayaan-1 Mission
Chandrayaan-1 was India’s first mission to the Moon and was launched on October 22, 2008. The primary objectives of Chandrayaan-1 were to create detailed maps of the lunar surface, study the distribution of elements, minerals, and water ice, and investigate the Moon’s atmosphere.
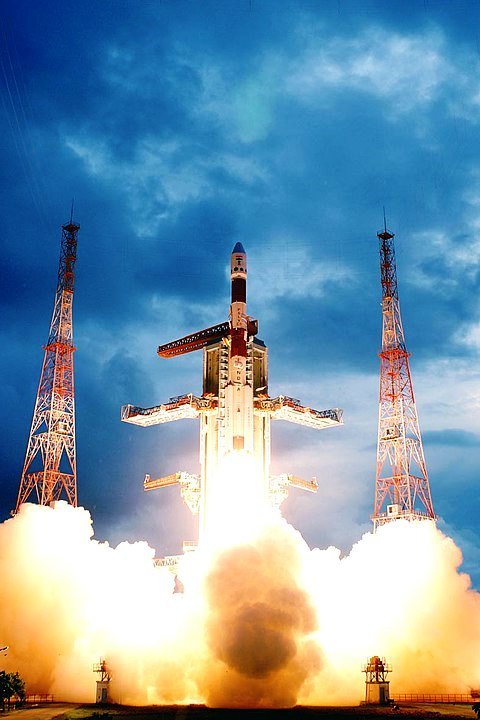

A. Payloads and Instruments:
Chandrayaan-1 carried a suite of scientific instruments, including:
- Terrain Mapping Camera (TMC): Captured high-resolution 3D images of the lunar surface.
- Hyper Spectral Imager (HySI): Mapped the lunar mineral resources.
- Lunar Laser Ranging Instrument (LLRI): Measured the distance between the Earth and the Moon.
- Moon Impact Probe (MIP): Released a probe that impacted the lunar surface, providing data on the Moon’s composition.
B. Key Discoveries and Achievements:
During its operational phase, Chandrayaan-1 achieved several important milestones:
- Confirmation of the presence of water ice on the Moon’s surface.
- Mapping of the Moon’s surface at unprecedented resolution.
- Identification of minerals, including magnesium, aluminum, calcium, and iron, on the lunar surface.
- Detection of the presence of helium-3, a potential fuel source, on the Moon.
II. Chandrayaan-2 Mission
Chandrayaan-2 was a more ambitious mission, comprising an orbiter, a lander, and a rover. It was launched on July 22, 2019, with the goal of landing a rover on the lunar surface and conducting scientific experiments.
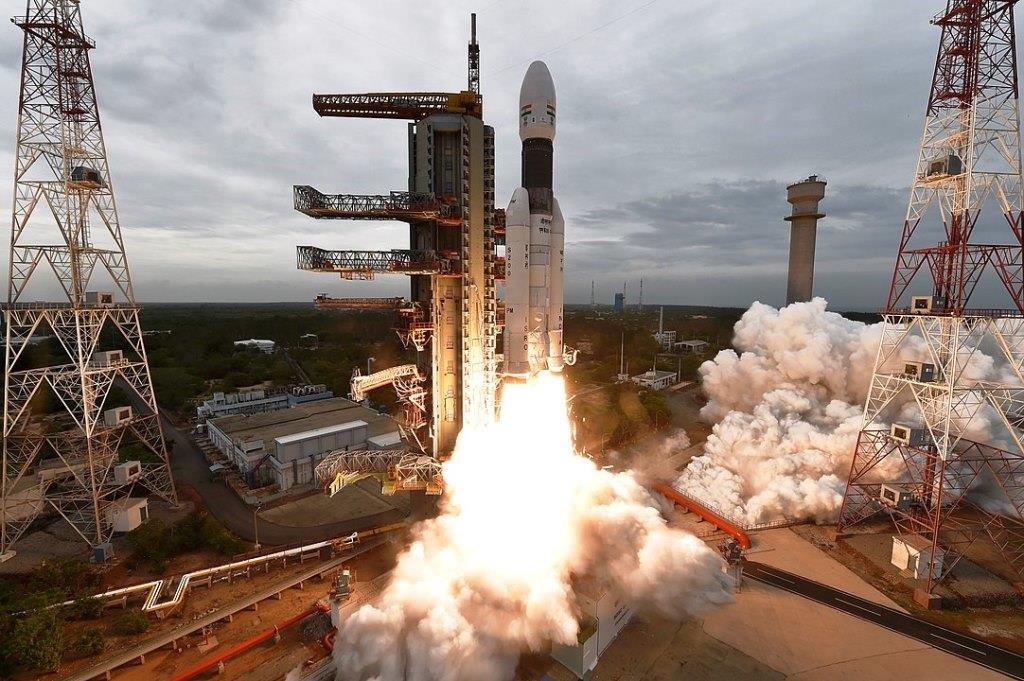

A. Mission Component:
Chandrayaan-2 consisted of the following components:
- Orbiter: Equipped with a suite of scientific instruments to study the Moon’s surface and atmosphere.
- Vikram Lander: Intended to make a soft landing on the lunar surface and release the Pragyan Rover.
- Pragyan Rover: Designed to traverse the lunar surface, collect data, and perform experiments.
B. Challenges and Achievements:
Although the mission encountered a setback during the landing phase, it achieved several significant milestones:
- Successful launch and orbit insertion of the spacecraft.
- High-resolution imaging and mapping of the lunar surface by the orbiter.
- Demonstration of India’s ability to navigate and control a spacecraft in lunar orbit.
- Advancement of technological capabilities in lunar landing and rover technology.
III. Overview Chandrayaan 1 and Chandrayaan 2 Mission
Chandrayaan-1 and Chandrayaan-2 have significantly contributed to the scientific understanding of the Moon and have bolstered India’s position in space exploration. These missions have yielded valuable data, including the discovery of water ice and minerals, and have provided important insights into lunar geology and the Moon’s atmosphere. The success of these missions has paved the way for future lunar exploration endeavors and further cemented India’s role in the global space community.
Read More Blogs:-SpaceX’s Starship Spacecraft Test Ends in Explosion
ISRO New Mission:- India’s Gaganyaan Mission: Challenges, Exploration & Triumphs





